Products
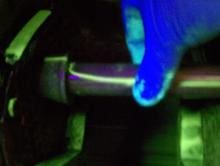
Magnetic Particle Inspection
This inspection method is used for detecting cracks, seams, laps, inclusions, welding flaws, and discontinuities on the surface of ferromagnetic materials.

Liquid Penetrant Inspection
This inspection method is generally used on aluminum, magnesium, and stainless steel. It can, however, be useful for other metals and materials. Detects cracks, discontinuities, corrosion, welding flaws, laps, cold shuts, and porosity

Passivation
It dissolves all traces of foreign materials, such as pieces of iron particles, tool scrapings, chips, etc., that will cause rust or stain spots if they are not removed. A thin, transparent passive film forms over the surface and prevents this condition from occurring. The presence of rust and/or heavy heat treatment may necessitate a pre-pickle. Our inspection personnel conduct the required copper sulfate test, salt spray and water immersion inspection tests in accordance with AMS-STD-753 and ASTM B117

+Anodizing
Sulfuric acid anodizing: Not to be applied to assemblies or parts with joints, or recesses that might entrap solution. Good electrical barrier and paint base. May be dyed in all colors. Dichromate seal, when specified, will impart a yellow color. Produces excellent decorative finishes when the part is either polished, brushed, or bright dipped prior to anodizing, good corrosion and abrasion resistance.

+Cadmium Finishing
The most commonly used finishing. The high density of the plate affords excellent corrosion resistance.
Type I coating is very susceptible to stains and fingerprints.
Type II coating is excellent for resistance to moisture and humidity and as a paint base. Chromate colors besides gold are clear, olive-drab and black treatment.
Type III is a good paint base.
Stress relief is required on metal with a hardness of Rockwell C34 or above, and hydrogen embrittlement reliefs are required after finishing on metal with a hardness of Rockwell C36 or above

+Electropolishing
This process is an electrolytic removal of metal from a highly ionic solution by means of an electrical potential and current, or, in other words, reverse electro finishing.

Chem Film
Chem Film, also called Chemical Film, is a chemical conversion coating. It typically refers to a chromate conversion coating applied to aluminum and its alloys. The chem film coating provides a layer of corrosion protection and a base for paint and primer.

Dry Lube
Dry Film Lubrication is a process whereby high performance coatings consisting of fine particles of lubricating agents are blended with special binders and additives. Once cured, these lubricating agents bond to the surface of the part as a solid film.

Glass and
Aluminum Oxide Blasting
Due to its high etch properties, its ability to be recycled and its fast working speed, aluminum oxide is an extremely popular media for blasting.
Glass blasting is gentler. It will not deform or cause damage to the parts.

Deburring and Tumbling
Deburring is a finishing process that removes sharp edges, burrs, fins, or inconsistencies from material, such as metals, steel and alloys, leaving the material with smooth edges and fine finished surfaces.

UVET
UVET's UV LED flood curing systems deliver uniform and powerful irradiation for repeatable and large area curing processes.


